Topology
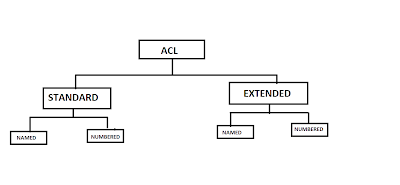
TOPOLOGY Arrangement of devices We are having two types of topologies. They are 1) Physical topology 2) Logical topology Physical Topology It means physical arrangement of devices. We are having five types of physical topologies. They are • Bus topology • Ring topology • Star topology • Tree topology • Mesh topology Logical Topology Logical arrangement of devices. We are having two models in logical topologies. They are • Workgroup model or peer to peer Model • Domain Model or client server model. Workgroup Model or Peer-Peer Model If you install any Operating System (client os/Server os). By default all the computers belongs to workgroup model. Work group model computers are standalone computers or individual computers. Workgroup model computers doesn’t depend on any other computers Workgroup model computers create “LOCAL USER ACCOUNTS”. For Local user account