ROUTING PROTOCOLS
Routing is the process of moving packets from one network to another network.
Routing involves two basic activities-
a)Determining best paths
b)Forwarding packets through these paths.
Conditions of routing:-
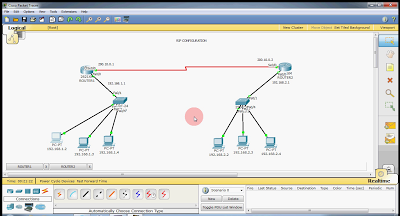
1)Router1 ethernet interface should be in the same network as your Router1 office LAN and similarly is the case with Router2 and its LAN.
2)Router1 and Router2 connected serial interface should be in the same network i.e., ip address
3)Router1 LAN and Router2 LAN should be in different networks.
4)All interfaces of a routers should be in different networks.
Types of Routing
1)Static Routing
2)Default Routing
3)Dynamic Routing
But we are going see Dynamic Routing first.
Dynamic Routing:-
Each router in dynamic routing, advertise to their neighbor router. For updating information, each router will have time outs based on routing protocol.
RIP(ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL):-
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C09NEMj8KJM
Routing involves two basic activities-
a)Determining best paths
b)Forwarding packets through these paths.
Conditions of routing:-
1)Router1 ethernet interface should be in the same network as your Router1 office LAN and similarly is the case with Router2 and its LAN.
2)Router1 and Router2 connected serial interface should be in the same network i.e., ip address
3)Router1 LAN and Router2 LAN should be in different networks.
4)All interfaces of a routers should be in different networks.
Types of Routing
1)Static Routing
2)Default Routing
3)Dynamic Routing
But we are going see Dynamic Routing first.
Dynamic Routing:-
Each router in dynamic routing, advertise to their neighbor router. For updating information, each router will have time outs based on routing protocol.
RIP(ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL):-
- Distance vector protocol
- Open Standard
- Uses Bellman-Ford algorithm
- Classful routing protocol
- Updates are periodically broadcasting using IP address 255.255.255.255.
- Complete routing table is sent as the update.
- Each update can contain a maximum of 25 routes.
- Administrative distance is 120
- Metric: Hop count-Max hop count
- Used for small networks
- Also known as Routing by Rumour
- Load balancing on 4 equal cost paths(Max 6 paths)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C09NEMj8KJM
Comments
Post a Comment